Frequent disconnection of the network adapter is a common issue during computer use, especially on Windows systems, where it troubles many users. An unstable internet connection not only affects the browsing experience but can also disrupt work and entertainment.
This article will thoroughly analyze the common causes of network adapter disconnections and provide a detailed step-by-step guide to help you resolve the issue and restore a stable internet connection.
I. Common Causes of Frequent Network Adapter Disconnections
Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers
Power management settings causing automatic shutdown
Weak or heavily interfered wireless signal
Router or network equipment failure
System updates or software conflicts
II. Detailed Troubleshooting Steps
1. Update the Network Adapter Driver
Outdated or damaged drivers are a major cause of persistent disconnection. Ensuring that your network adapter driver is up to date can effectively resolve this issue. To avoid installation errors, it is recommended to use Driver Talent X to scan and automatically update all drivers with one click, ensuring compatibility and up-to-date versions.
Click the button below to download the latest version of Driver Talent X, install and launch the software.
In the "Drivers" section, select "Scan" and click the "Scan" button. The software will automatically detect the status of all drivers on your computer.
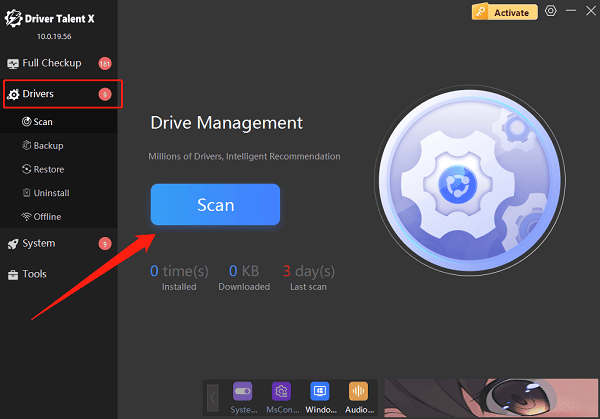
Locate the network driver in the scan results and click the "Upgrade" button.
After the update is complete, restart your computer to ensure the driver takes effect.
2. Disable Power Management to Prevent Auto Shut-off
Press Win + X and open Device Manager.
Right-click your network adapter device and select "Properties".
Switch to the "Power Management" tab.
Uncheck the option "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power".
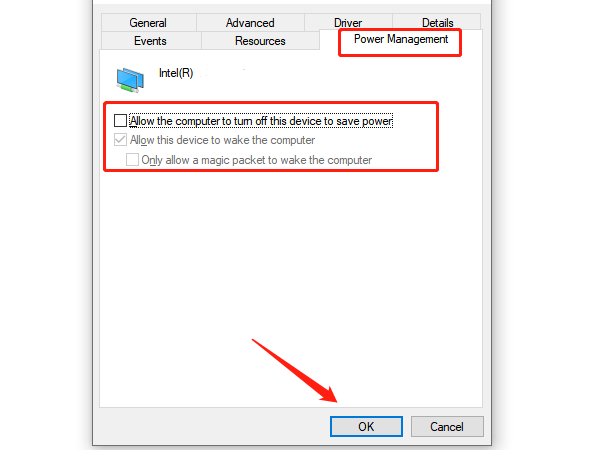
Click "OK" to save the settings.
3. Optimize Wireless Network Environment
Place the router in an open area, avoiding obstructions from walls or metal objects.
Log in to the router's control panel (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
Go to the wireless settings and change the wireless channel to one with less interference (such as 1, 6, or 11).
Use your computer to check Wi-Fi signal strength and ensure it is stable.
4. Restart Network Devices
Power off the modem and router, then wait 1–2 minutes.
Turn on the modem first, wait for it to fully boot up, then power on the router.
Wait for the devices to complete self-check, then reconnect to the network.
5. Reset Network Settings
Press Win + I to open the Settings menu.
Click "Network & Internet", then select "Status".
Scroll to the bottom and click "Network reset".
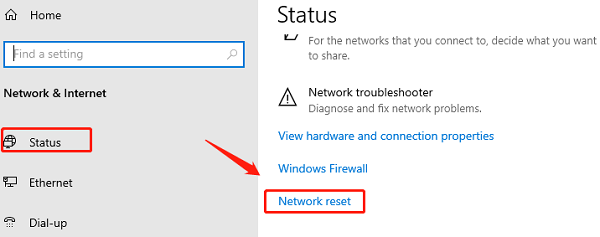
Click "Reset now" and confirm the action.
Your computer will restart automatically and complete the reset.
6. Check Firewall and Antivirus Settings
Temporarily disable the firewall:
Press Win + R, type "control", and press Enter to open the Control Panel.
Select "System and Security" > "Windows Defender Firewall".
Click "Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off", then choose to turn it off.
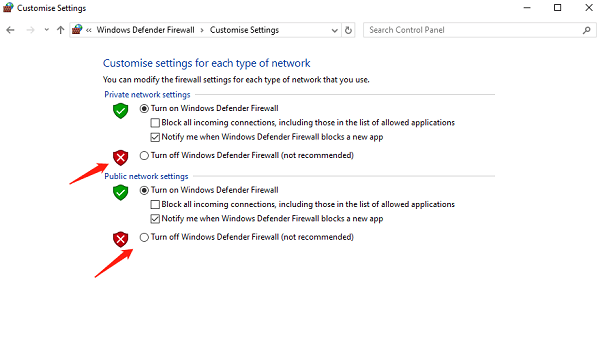
Disable third-party security software:
Open your antivirus program and temporarily disable the protection feature.
Check if the network becomes stable.
If it does, adjust the firewall or antivirus settings to avoid unnecessary blocking.
7. Run the Network Troubleshooter
Press Win + I to open Settings.
Go to "Update & Security" > "Troubleshoot".
Click "Additional troubleshooters", find "Network Adapter", and click "Run the troubleshooter".
Follow the prompts to complete the scan and repair process.
Frequent network adapter disconnections can stem from various causes, but most issues can be resolved using the detailed steps above. It is recommended to prioritize updating drivers and adjusting power management settings, followed by optimizing the network environment and checking system configurations. These steps can significantly improve network stability. If the problem persists after trying all solutions, consider contacting your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or seeking professional technical support.
