In the Windows system, ntoskrnl.exe is a core system process responsible for managing memory, process scheduling, and the hardware abstraction layer. Under normal circumstances, it does not consume a large amount of disk resources.
However, some users have found that ntoskrnl.exe causes excessively high disk read/write activity, resulting in system lag, slow response, and even affecting daily operations. This article will comprehensively analyze the common causes of high disk usage by ntoskrnl.exe and provide multiple practical solutions to help you easily fix the problem.
Common Causes of High Disk Usage by ntoskrnl.exe
Driver conflicts or corruption: Outdated or incompatible drivers may cause the system kernel to frequently access the disk.
System file corruption: Abnormal system files that ntoskrnl.exe depends on can trigger high disk read/write.
Disk bad sectors or hardware failure: Disk problems can cause the system to repeatedly attempt read/write operations, indirectly causing excessive ntoskrnl.exe activity.
Virus or malware infection: Some malicious programs disguise themselves as ntoskrnl.exe or use it to perform abnormal operations.
Windows update issues: Update stalls or file conflicts may cause the kernel process to frequently access the disk.
Background programs consuming resources: Some applications or services that frequently interact with the system kernel can cause increased disk usage.
Practical Solutions for High Disk Usage by ntoskrnl.exe
1. Check for device driver updates
Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers are a primary cause of high disk usage. It is recommended to use the Driver Talent X tool, which saves time and effort and avoids the risk of downloading or installing incorrect drivers.
Click the download button to get the latest Driver Talent X, install and launch the software.
In the "Drivers" tab, select "Scan", and the software will automatically detect the status of all drivers on your computer.
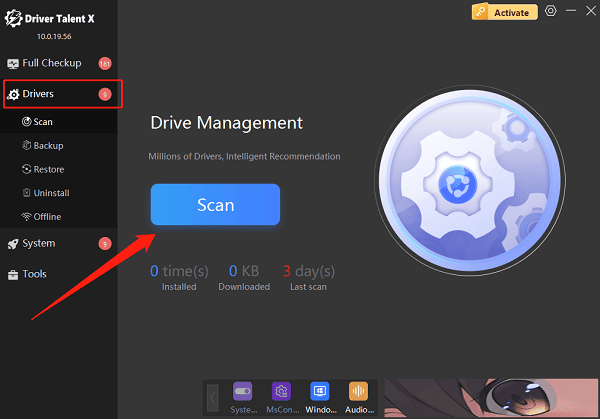
Find the drivers that need updating and click the "Upgrade" button.
Restart your computer after updating to ensure the driver takes effect.
2. Check system files
Open Command Prompt with administrator privileges:
Type cmd in the Windows search bar.
Right-click "Command Prompt" and select "Run as administrator".
Run the SFC scan:
In the Command Prompt, enter: sfc /scannow and press Enter.
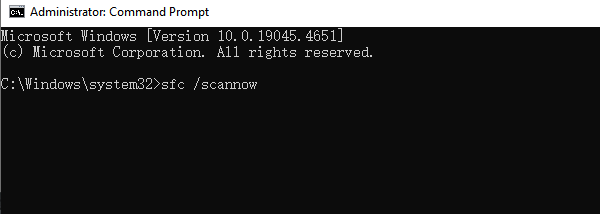
Wait for the scan to complete and automatically repair damaged files.
Run the DISM tool (if SFC didn't fix the issue):
Enter the following command: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
After completion, restart your computer to apply the repair.
3. Check disk health status
Open Command Prompt as administrator (see above).
Enter: chkdsk C: /f /r and press Enter.
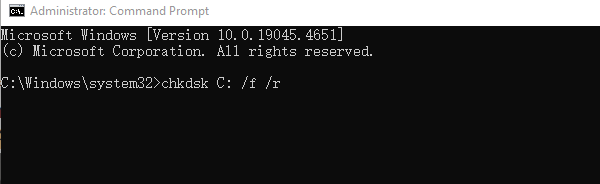
When prompted to check the disk on the next restart, enter "Y" and press Enter.
Restart your computer, and the system will check and repair the hard drive.
4. Scan for viruses and malware
Use Windows Defender or third-party antivirus software to perform a full scan and eliminate viruses or trojans.
Open Windows Security Center.
Select "Virus & threat protection" and click "Quick scan" or "Full scan".
Check for any suspicious processes or files.
5. Disable the Indexing Service
Disabling the indexing service can reduce system resource usage.
Press Win + R, type "services.msc", and press Enter.
Find "Windows Search" in the service list.
Right-click "Windows Search", select "Properties".
Set "Startup type" to "Disabled", then click "Stop".
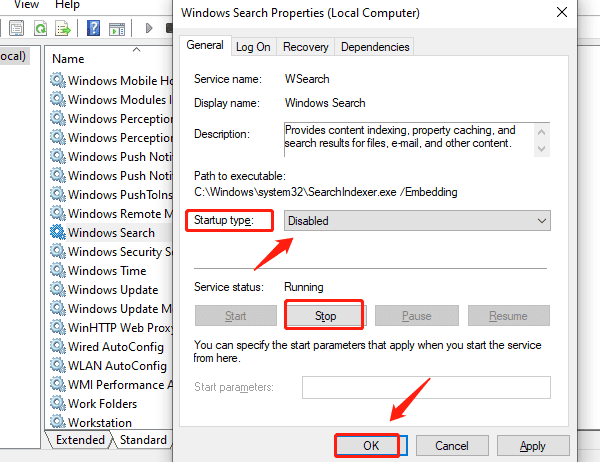
Click "OK" to save the settings.
6. Disable Runtime Broker
Disabling Runtime Broker can reduce system resource consumption.
Press Win + R, type "regedit", and press Enter.
Navigate to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\TimeBrokerSvc
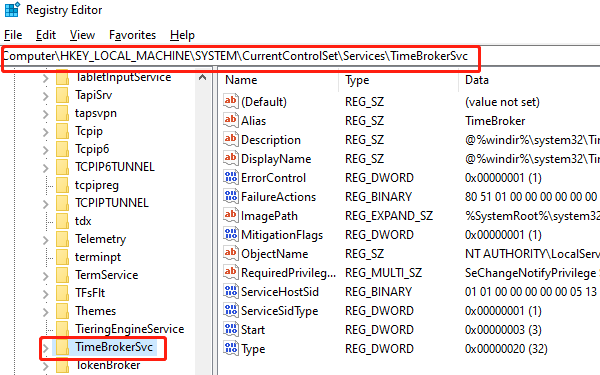
Find the "Start" entry in the right pane and double-click it.
Change the value data to "4", click "OK".
Close the Registry Editor and restart the computer.
7. Close unnecessary background programs and services
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
Sort by the "Disk" column to identify high disk usage processes.
Right-click and choose "End task", then observe system responsiveness.
8. Check Windows Update status
Ensure system patches are fully installed to avoid update stalls.
Go to "Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update".
Click "Check for updates" and install all recommended patches.
Restart the computer and check if the issue is resolved.
As a key component of the Windows kernel, abnormal disk usage by ntoskrnl.exe usually indicates underlying system or hardware problems. By updating drivers, repairing system files, checking the hard drive, and removing malware, most high disk usage issues can be effectively resolved.
If problems persist, it is recommended to contact professional technical support for further hardware diagnostics. Additionally, using the Driver Talent X intelligent driver management tool to keep device drivers up to date can greatly reduce the risk of system anomalies caused by driver issues.
