When using a Windows computer, many users encounter a frustrating issue: the WiFi shows as connected, but there's no internet access. Web pages won't load, and the network icon displays a yellow exclamation mark. Although this problem may seem complicated, it can often be resolved effectively through a few simple steps.
This article will walk you through the common causes of this issue and provide a range of practical solutions to help you quickly restore your internet connection.
Common Causes of "WiFi Connected but No Internet"
Before attempting any fixes, it's crucial to understand the possible causes of the issue:
Faulty or outdated network drivers
Malfunctioning router or modem
Incorrect or unresponsive DNS settings
IP address conflicts
Firewall or security software blocking internet access
Network configuration issues caused by system updates
Basic Troubleshooting Steps
1. Restart Your Router and Computer
Power off the router and wait a few minutes before turning it back on.
Restart your computer as well and check if the internet connection is restored.
2. Try Connecting Other Devices
Use a phone or another computer to connect to the same WiFi network.
If other devices also can't access the internet, the issue likely lies with your router or broadband connection.
Comprehensive Fixes (for Windows Systems)
1. Update Network Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers are a common cause of network issues. Updating your network drivers can be an effective solution. If you're unsure about your hardware model or not familiar with manual driver installation, it's recommended to use a tool like Driver Talent X—saving you time and helping avoid downloading the wrong drivers.
Click the button below to download the latest version of Driver Talent X, then install and launch it.
Go to the "Drivers" tab and click "Scan". The software will automatically detect the status of all drivers on your computer.
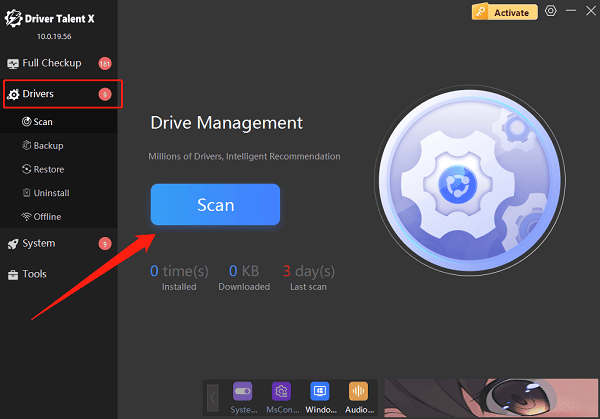
Locate the network driver in the scan results and click the "Upgrade" button.
After the update, restart your computer to apply the changes.
2. Change DNS Server Address
Press Win + R, type "ncpa.cpl", and press Enter to open "Network Connections".
Right-click your current WiFi connection and select "Properties".
Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties".
Choose "Use the following DNS server addresses" and enter:
Preferred DNS server: 8.8.8.8
Alternate DNS server: 8.8.4.4
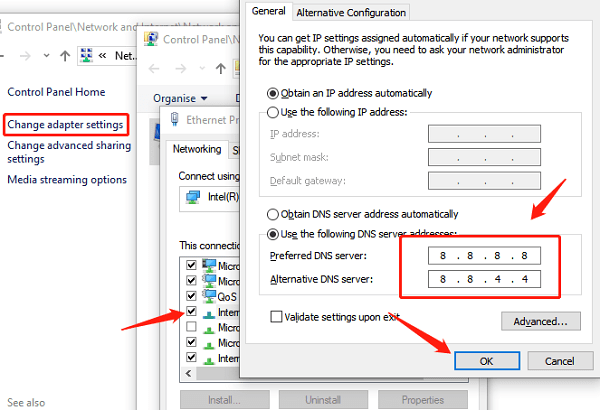
Click "OK" and then restart the network connection.
3. Reset Network Settings
Press Win + I to open the Settings menu.
Go to "Network & Internet" and select "Status" from the left menu.
Scroll down and click the "Network reset" button.
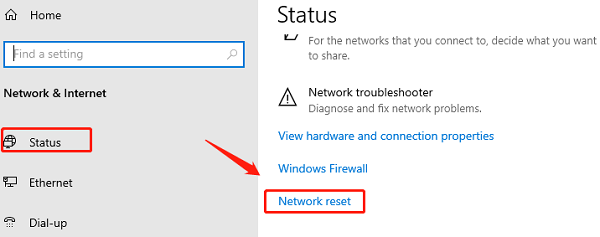
Click "Reset now" and confirm. This will remove and reinstall all network adapters and reset settings to default.
Your computer will automatically restart. Check if the connection is restored.
4. Run Network Troubleshooter
Press Win + I to open the Settings menu.
Go to "Update & Security" and click "Troubleshoot" from the left menu.
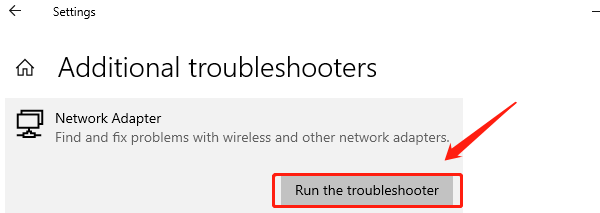
On the "Troubleshoot" page, click "Additional troubleshooters".
Find "Network Adapter" and click "Run the troubleshooter". Windows will scan for network issues and attempt to fix them.
After completion, check your internet connection.
5. Disable Firewall or Third-Party Security Software
Sometimes, firewalls or antivirus programs may mistakenly block network access:
Temporarily disable Windows Defender Firewall or any third-party software.
Check if the internet connection is restored.
If the software is the cause, adjust its settings or consider switching to a different program.
Still Not Working? Try These Advanced Methods
Check if MAC address filtering is enabled on your router.
Log in to your router's admin panel to see if device access is restricted.
Try assigning a static IP address to your computer (requires knowledge of network configuration).
Use a mobile hotspot to test whether your PC's network adapter is working properly.
Although the "WiFi connected but no internet" issue may seem difficult to resolve, it's rarely caused by hardware damage. By following the troubleshooting steps in this guide, you can usually fix it on your own.
We recommend using Driver Talent X to quickly identify driver-related problems and boost your repair efficiency. If the issue persists, contact your internet service provider or a technical support professional for further assistance.
