Is svchost.exe using too much CPU on your Windows PC? Learn how to identify the cause and fix high CPU usage with 12 proven methods, including stopping services, scanning for malware, and optimizing system settings.
When svchost.exe is hogging CPU resources, it can bring even the most powerful systems to a crawl. This problem, although common in Windows, is often misunderstood. In this guide, we provide an in-depth analysis of why svchost uses so much CPU, and how to fix it efficiently.
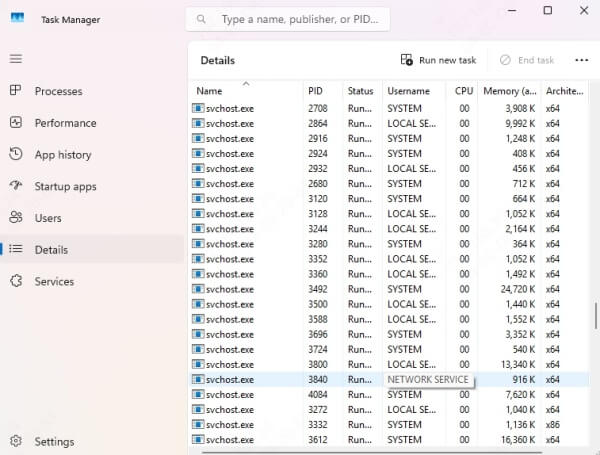
Part 1. What Is svchost.exe and Why Is It Running Multiple Instances?
svchost.exe (Service Host) is a system process used to host multiple Windows services. It’s designed to optimize system resource usage, grouping services that require similar resources.
Each svchost.exe process represents a service group, meaning you may see multiple instances running in Task Manager. That’s normal. But when one of these processes starts consuming too much CPU, it's often because one of the underlying services is malfunctioning.
Common Reasons Why svchost.exe Hogging CPU
Understanding the root cause is key to fixing it. Below are the most common culprits:
Windows Update service stuck
Superfetch (SysMain) service
Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
Malware camouflaged as svchost.exe
Corrupt Windows system files
WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) issues
Part 2. How to Fix svchost Hogging CPU
1. Use Task Manager to Find the Problematic svchost.exe
Before applying any fixes, it's crucial to identify exactly which svchost.exe process is causing the high CPU usage. The Task Manager gives you a direct way to investigate the services running under each svchost instance. By pinpointing the exact culprit, you avoid random trial-and-error and move toward a targeted solution.
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager
Click on the Details tab

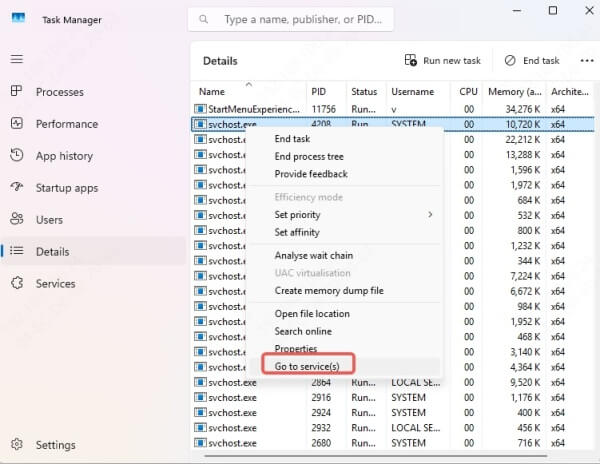
Locate any svchost.exe entries with high CPU usage
Right-click it and choose “Go to Service(s)”
The “Services” tab will highlight which services are running under that svchost
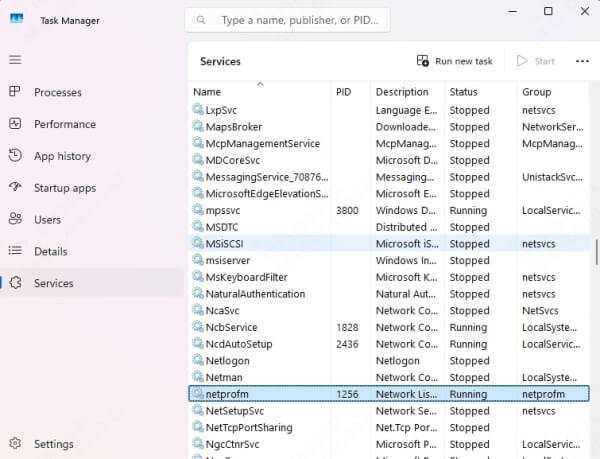
Take note of the services shown. One or more of these are likely causing the spike.
2. Stop the Problematic Service Temporarily
Once you've identified the problematic service within svchost, temporarily stopping that service can immediately reduce CPU usage. This is a quick and non-invasive way to test whether a specific service is the root cause of the spike.
1. Open Services via Run (services.msc)
2. Locate the service
3. Right-click > Stop
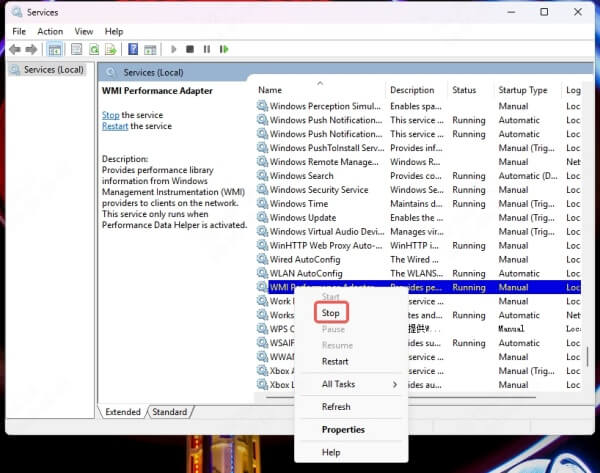
4. Common services to try stopping:
wuauserv (Windows Update)
BITS
SysMain
WMI
Note: Only stop services you understand. Some are essential for Windows functionality.
3. Disable Windows Update Temporarily (If It’s the Culprit)
In many cases, the Windows Update service (wuauserv) is the biggest contributor to svchost CPU spikes. When updates get stuck or the update process misbehaves, it can consume excessive CPU cycles. Temporarily disabling Windows Update can bring quick relief, especially if you're not actively installing patches.
To disable it:
sc stop wuauserv
sc config wuauserv start= disabled
To re-enable it later, use:
sc config wuauserv start= auto
sc start wuauserv
4. Scan for Malware Masquerading as svchost.exe
Malicious programs often disguise themselves as svchost.exe to remain hidden and run unauthorized tasks in the background. If a malware infection is to blame, no amount of service tweaking will help — you need to eliminate the threat entirely. Scanning your system with both built-in and third-party tools is critical.
Steps to scan:
Run Windows Defender Full Scan
Use third-party tools like Malwarebytes for deep scans
Use Process Explorer from Sysinternals to verify if svchost.exe is running from C:\Windows\System32\
Any instance running from outside that folder is suspicious and should be treated as malware.
5. Fix Corrupted System Files
System file corruption is another hidden cause of svchost-related CPU spikes. Damaged or missing core files may prevent services from running properly, forcing Windows into a loop of retries and failures — all consuming precious CPU resources. Running a system integrity check is a safe and effective way to correct these problems.
Open Command Prompt as Administrator and run:
sfc /scannow
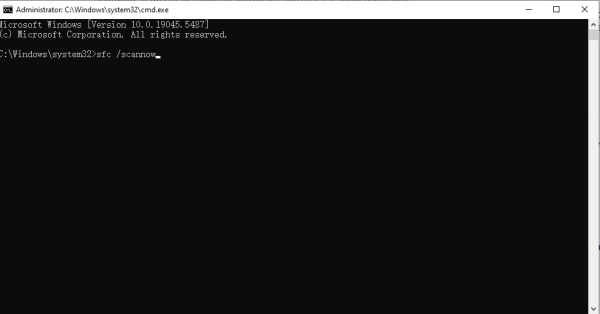
Then, run:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
These commands check for and repair any corrupt files that could be causing CPU spikes.
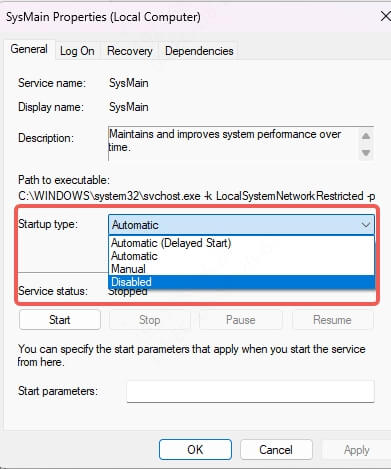
6. Disable Superfetch (SysMain)
The Superfetch service (now called SysMain) preloads frequently used apps into RAM for faster access, but it can backfire on systems with limited memory or SSDs. In such scenarios, Superfetch can cause svchost.exe to overload the CPU during background operations. Disabling it helps reclaim performance.
To disable:
Open Services (services.msc)
Find SysMain
Right-click > Stop
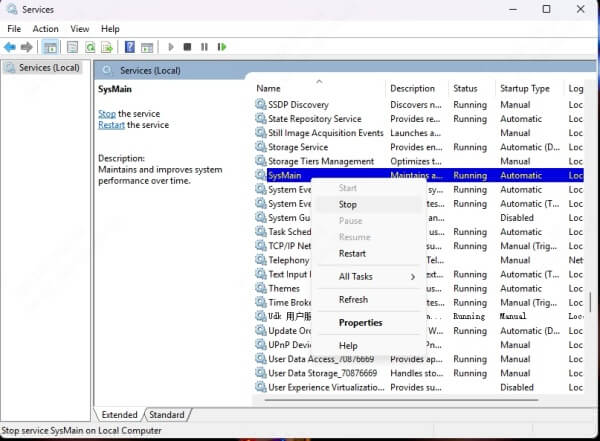
Set Startup Type to Disabled
7. Adjust Windows Performance Settings
Sometimes, your system’s performance settings are simply too aggressive or unnecessary. Visual effects and background activities can weigh down your CPU through svchost-managed services. By adjusting performance settings, you ease the load and give svchost fewer processes to manage.
Go to Control Panel > System > Advanced System Settings
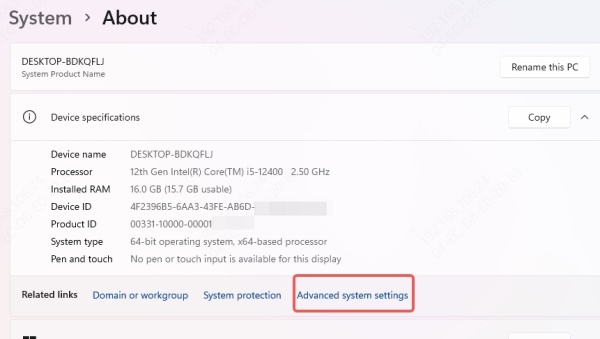
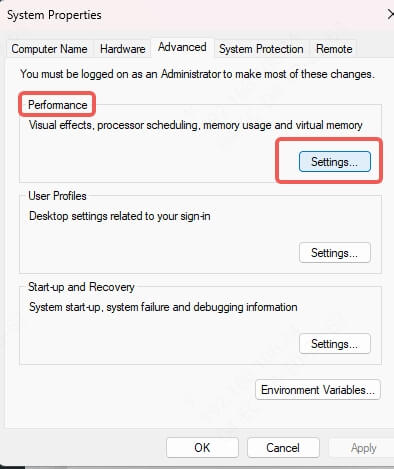
Under Performance, click Settings
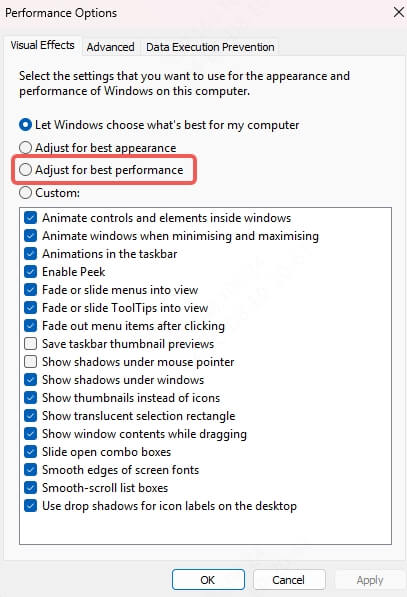
Choose Adjust for best performance or manually disable effects you don’t need
8. Monitor svchost.exe Using Resource Monitor
If the cause of the issue still isn't obvious, Resource Monitor offers a deeper look into CPU activity, process dependencies, and services tied to svchost.exe. This tool allows you to track exactly which files, handles, or threads are being used — making it easier to pinpoint the offending resource.
Press Win + R, type resmon
Go to the CPU tab
Expand svchost.exe
Analyze associated handles and modules
9. Upgrade Drivers and BIOS
Outdated or buggy drivers and BIOS versions can introduce incompatibilities that stress svchost.exe, especially with hardware-related services. Ensuring your drivers and firmware are current can prevent unnecessary CPU cycles from being wasted due to inefficient system communication.
Use Device Manager to update critical drivers
Visit your motherboard/laptop manufacturer’s website to get the latest BIOS update
Pro Tip: Use tools like Driver Talent X to automate updates safely.
Conclusion
When svchost.exe is hogging CPU, it’s a symptom — not the root problem. By following a methodical approach, identifying the service responsible, and using the above fixes, you can regain control over your system’s performance. Never ignore high CPU usage; it can shorten your hardware’s lifespan and waste energy.
If you need to fix driver issues or optimize your PC system, don't hesitate to give Driver Talent Xa try!
