A chipset driver is a crucial component in ensuring your computer’s motherboard and operating system communicate effectively. Without the correct chipset drivers, your PC could experience performance issues, hardware malfunctions, or fail to recognize vital system components. This article dives deep into what a chipset driver is, what it does, how to find and check its version, and why keeping it updated is essential for system stability and speed.
Part 1. What Is a Chipset Driver?
A chipset driver is a software package that allows your operating system to interact with the motherboard chipset of your computer. The chipset is a collection of integrated circuits that manage the data flow between the processor, memory, storage devices, graphics cards, and peripherals.
Typically, chipsets are manufactured by companies like Intel, AMD, or NVIDIA, and the drivers provided are tailored to support specific features of that chipset. These drivers unlock functionalities such as:
USB ports
SATA and NVMe storage controllers
PCI Express lanes
Onboard audio and network cards
Power management features
Without proper chipset drivers, your system might not function optimally or could even miss out on hardware capabilities.
Part 2. What Does a Chipset Driver Do?
The chipset driver acts as the communication bridge between your hardware and the operating system. It provides low-level control for many vital motherboard functions.
Here's a detailed look at what chipset drivers enable:
1. Memory Management
The chipset controls how data flows between the CPU and RAM. The driver ensures optimal memory mapping and bandwidth usage.
2. PCIe and Expansion Slot Communication
Your GPU, SSDs, and other expansion cards connect to the motherboard via PCIe lanes. The chipset driver manages how these components communicate, ensuring proper speed and stability.
3. Integrated Peripherals
Motherboards often include built-in audio chips, Ethernet ports, and USB controllers. The chipset driver activates and controls these elements, often improving performance and enabling advanced features.
4. Power Management
Modern chipsets support power-saving technologies like C-states and dynamic frequency scaling. Chipset drivers help the OS manage energy usage efficiently, which is critical for laptops and desktops alike.
5. SATA and NVMe Controller Configuration
Storage device speeds and compatibility depend heavily on how the chipset communicates with SATA and M.2 interfaces. A proper driver ensures your SSD or HDD operates at full potential.
Part 3. How to Check Chipset Driver Version in Windows
Keeping your chipset driver up to date is essential for hardware compatibility and system performance. Here’s how you can check your chipset driver version:
Method 1: Using Device Manager
1. Press Windows + X and select Device Manager.
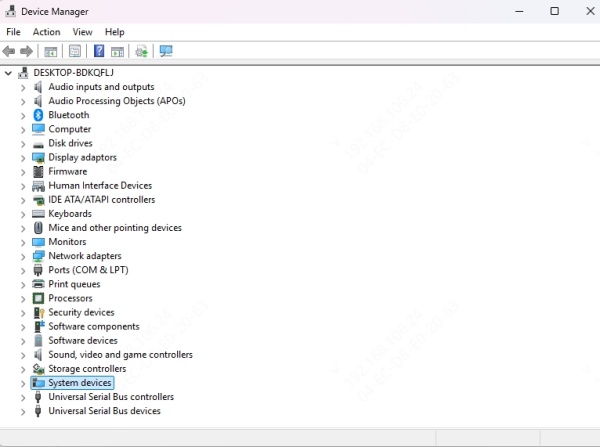
2. Expand System Devices.
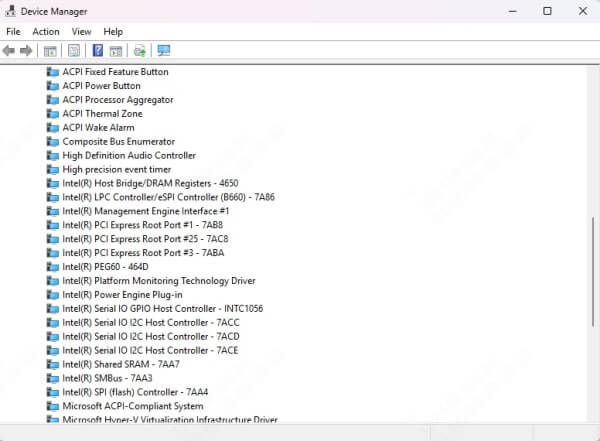
3. Look for entries like:
Intel(R) Chipset Device Software
AMD SMBus
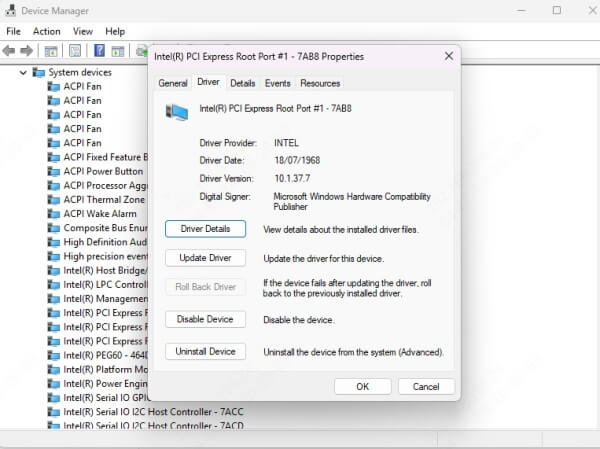
4. Right-click on the chipset device and choose Properties.
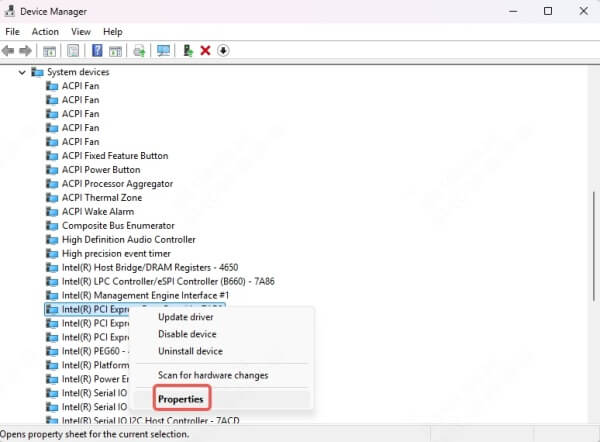
5. Under the Driver tab, check the Driver Version and Driver Date.
Method 2: Using Command Prompt
You can use WMIC to extract driver info:
wmic sysdriver where "name like '%%chipset%%'" get name, state, startmode
This may give limited data but is useful for quick checks.
Method 3: Use Third-Party Tools
Tools like Driver Talent X can help you identify outdated chipset drivers quickly and suggest updated versions.
Part 4. How to Find and Download the Latest Chipset Driver
If you need to update or reinstall your chipset driver, follow these steps to ensure you get the correct version for your system.
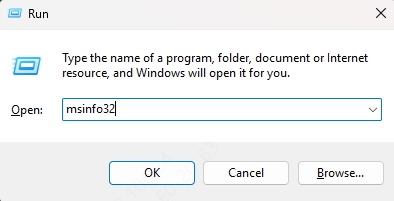
Step 1: Identify Your Motherboard Model
Press Windows + R, type msinfo32, and hit Enter.
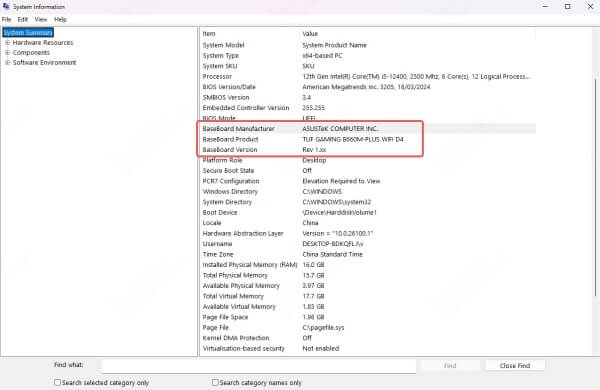
Under System Summary, check the BaseBoard Manufacturer and BaseBoard Product fields.
Step 2: Visit the Manufacturer’s Website
For Intel-based systems, visit Intel Download Center
For AMD-based systems, visit AMD Drivers and Support
For custom-built PCs, go to your motherboard manufacturer’s support page (e.g., ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte).
Step 3: Download and Install
Download the latest chipset driver matching your OS version (Windows 10, 11, 64-bit, etc.).
Run the installer and follow on-screen prompts.
Restart your system after installation to ensure changes take effect.
Why It’s Important to Keep Chipset Drivers Updated
Outdated chipset drivers can cause:
Hardware detection errors
USB or PCIe devices not functioning
Reduced SSD or RAM performance
Random system crashes or freezes
Updating to the latest chipset drivers ensures:
Compatibility with the latest Windows updates
Support for new hardware and peripherals
Better system stability and performance
Resolved known bugs and vulnerabilities
Final Thoughts
Your chipset driver is one of the most fundamental drivers on your system. Keeping it updated ensures optimal communication between your CPU, motherboard, RAM, and peripherals, leading to improved performance, fewer crashes, and extended hardware life.
And if you have encountered any driver issues, don't hesitate to download Driver Talent X to try!
