In Windows, explorer.exe is a critical process responsible for managing the desktop, taskbar, and File Explorer. However, it can sometimes consume excessive memory, causing system slowdowns or lag.
This article explains the common causes of high memory usage by explorer.exe and offers practical solutions to help restore smooth system performance.
1. What is explorer.exe?
explorer.exe is the File Explorer process in Windows. It also controls essential interface elements like the desktop, taskbar, and Start menu. As a key bridge between the user and the system, any issues with this process can directly affect the user experience.
2. Common Causes of High Memory Usage by explorer.exe
Resource-heavy folders or file previewing:
Opening folders containing large files, videos, images, or special file formats may trigger explorer.exe to load thumbnails and previews, significantly increasing memory usage.
Conflicts or errors with third-party Shell extensions:
Some installed software adds Shell extensions (e.g., context menu options or icon overlays). Incompatible or corrupted extensions can cause memory leaks in explorer.exe.
Virus or malware infection:
Certain viruses disguise themselves as explorer.exe or inject malicious code into it, leading to abnormal memory consumption.
Corrupted system files or registry errors:
Missing or corrupted system files and incorrect registry settings can interfere with the normal operation of explorer.exe.
Memory leaks:
Some Windows versions or patches may have memory leak issues that cause explorer.exe's usage to increase over time.
3. Solutions to Fix High Memory Usage by explorer.exe
Method 1: Check for Driver Updates
Drivers are a critical foundation for system stability. Using a professional driver management tool like Driver Talent X is recommended, it can automatically detect, download, and install the most suitable drivers for your device with high efficiency.
Click the Download button to get the latest version of Driver Talent X. Install and launch the software.
Under the "Drivers" section, select Scan and click "Scan" again. The tool will detect the status of all drivers on your PC.
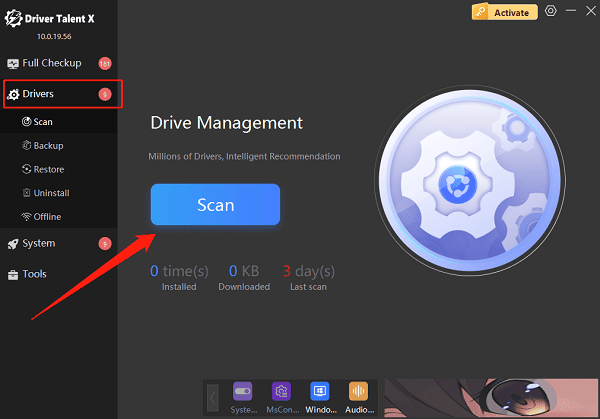
Click "Upgrade" next to any outdated drivers found in the scan results.
Restart your computer after updates to ensure changes take effect.
Method 2: Restart the explorer.exe Process
Open Task Manager, locate "Windows Explorer".
Click the "Restart" button at the bottom right.
This will refresh the File Explorer and clear temporary memory usage, providing a short-term fix.
Method 3: Clean Up Problematic Folders
Disable thumbnail previews: Go to the "View" tab and check "Always show icons, never thumbnails".
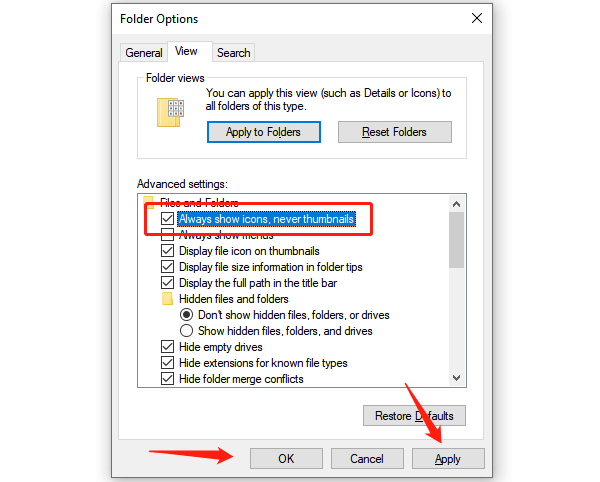
Turn off Preview and Details panes: In File Explorer, click "View" and disable both panes.
Method 4: Disable or Remove Problematic Shell Extensions
Download and run ShellExView.
Sort items by vendor or type and disable non-Microsoft context menu extensions.
Restart explorer.exe and observe if memory usage drops.
If a specific extension is found to be problematic, consider uninstalling the related software.
Method 5: Run System File Checker
Press Win + S, type "cmd".
Right-click Command Prompt and choose "Run as administrator".
Enter the following command and press Enter: sfc /scannow
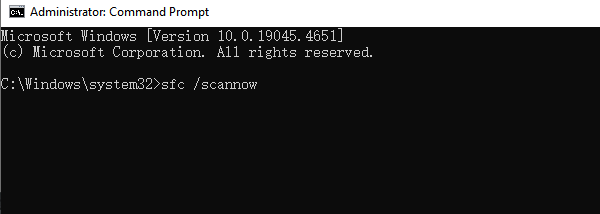
Wait for the system to scan and repair corrupted files.
Method 6: Update Windows System
Click the Start button, go to Settings > Update & Security.
In the "Windows Update" section, click "Check for updates".
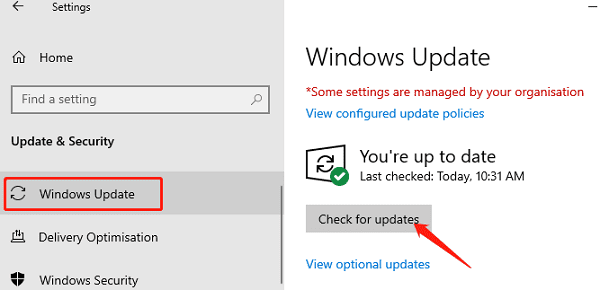
If updates are available, click "Download and install". Windows will install any new drivers or patches.
Restart your PC after installation.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Will restarting explorer.exe cause data loss?
A: No. Restarting Windows Explorer only refreshes the interface, it won't affect unsaved data.
Q2: What if the context menu has fewer options after disabling Shell extensions?
A: Only non-Microsoft extensions are disabled, so essential functions remain intact. You can re-enable items one by one if needed.
Q3: What if the System File Checker doesn't fix the issue?
A: Consider resetting or upgrading the system, or consult a professional technician for further troubleshooting.
High memory usage by explorer.exe is a common issue that can affect the smooth performance of a Windows system.
By updating device drivers, restarting File Explorer, and cleaning up problematic folders or extensions, most related problems can be resolved effectively.
It's recommended that users regularly maintain their system and use File Explorer wisely to ensure a stable and responsive computer experience.
