Have you ever opened Device Manager only to find your GPU mysteriously missing? It’s frustrating, especially if you’re trying to update drivers or troubleshoot laggy performance. This guide breaks down the exact steps you need to take when your GPU is not showing up in Device Manager.
Basic Pre-Checks
Before diving into advanced troubleshooting, it's wise to eliminate basic but common issues that can prevent the GPU from being detected. These simple checks could save you a lot of time.
Restart Your Computer
Yes, it sounds cliché, but a simple restart can often solve weird glitches—like your GPU not showing up.
Check Physical Connection of the GPU
Open your PC case and make sure your graphics card is seated properly in the PCIe slot. Also, ensure all power connectors are firmly attached. Loose cables or a slightly misaligned card can be enough to prevent detection.
Make Sure the Monitor Is Plugged into the GPU Port
Sometimes, people mistakenly plug the display cable into the motherboard instead of the GPU. Make sure it’s connected to your graphics card’s HDMI or DisplayPort.
Fix 1. Check Device Manager for Hidden Devices
Sometimes, your GPU might actually be listed in Device Manager but hidden or marked as inactive due to system misconfiguration. This step helps uncover such hidden devices.
How to Reveal Hidden Devices
In Device Manager:
Click View > Show hidden devices.
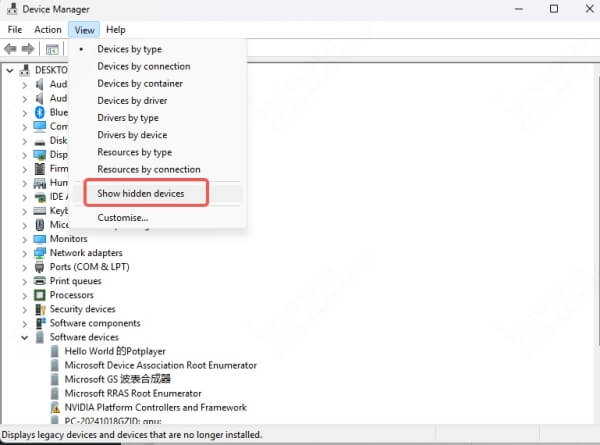
Look under Display adapters or Other devices.
Scan for Hardware Changes
Still can’t see it? Click on Action > Scan for hardware changes. Windows will recheck and try to recognize any new components.
Fix 2. Update or Reinstall GPU Drivers
Corrupt, outdated, or missing GPU drivers can prevent Windows from detecting the graphics card. Updating or reinstalling them can often resolve the issue.
Method 1: Use Device Manager
Open Device Manager.
Expand Display adapters.
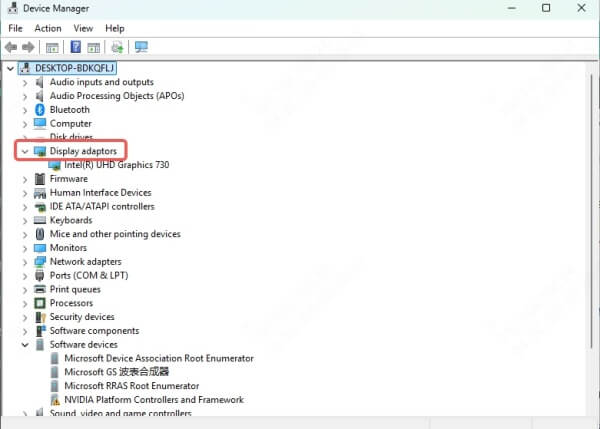
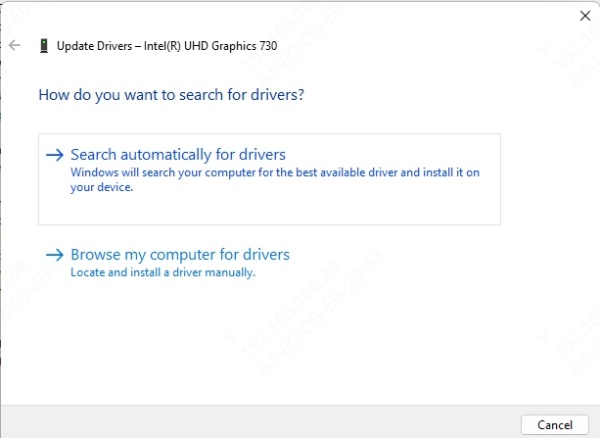
Right-click your GPU (if visible) and click Update driver.
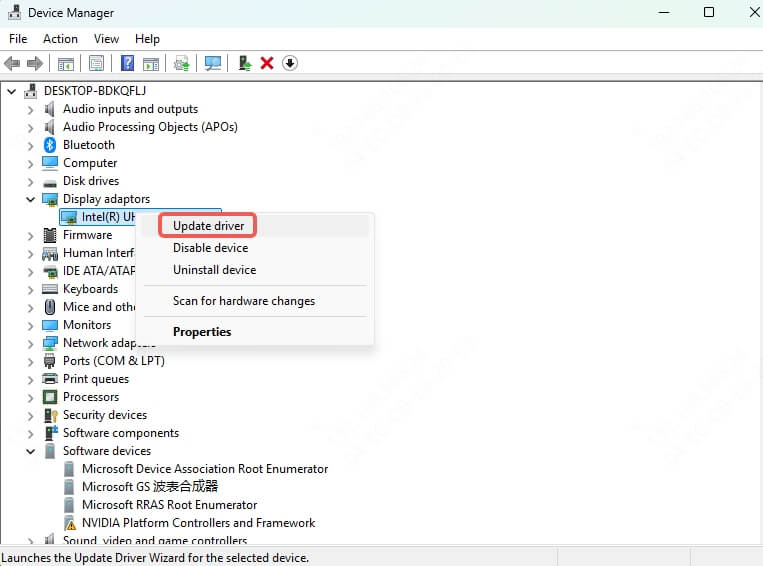
Select Search automatically for updated driver software.
Method 2: Use Manufacturer Website
1. Visit your GPU manufacturer’s website:
NVIDIA: https://www.nvidia.com/Download/index.aspx
AMD: https://www.amd.com/en/support
Intel: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/download-center/home.html
2. Download the latest drivers for your model.
3. Install and restart your system.
Recommended Tool: Driver Talent
Use a professional tool like Driver Talent to automatically detect and install missing or outdated drivers:
Step 1. Download and install Driver Talent.
Step 2. Click Scan to detect driver issues.
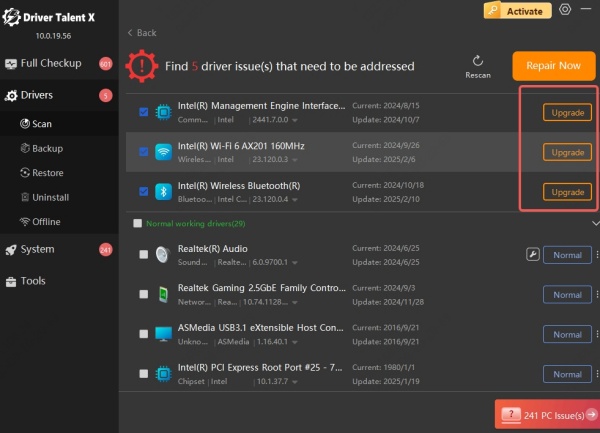
Step 3. Click Upgrade to download and install the latest drivers.
Step 4. Reboot your PC.
You can also uninstall the display driver using Uninstall feature in Driver Talent. Then scan and install the driver again.
Fix 3. Use Windows Troubleshooter
If you're not sure where to start or suspect a Windows-related error, the built-in troubleshooter can automatically detect and resolve common hardware problems, including GPU issues.
How to Run the Troubleshooter
Go to: Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Additional troubleshooters > Hardware and Devices
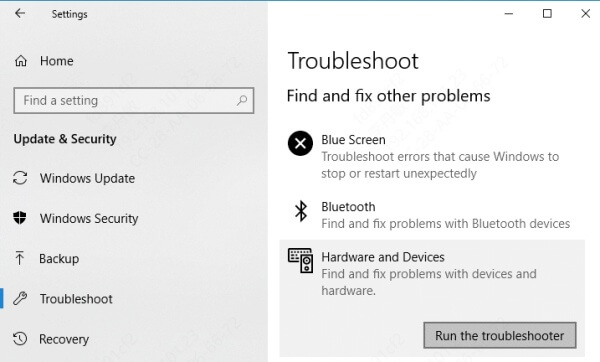
This will let Windows detect any underlying problems related to your hardware, including GPUs.
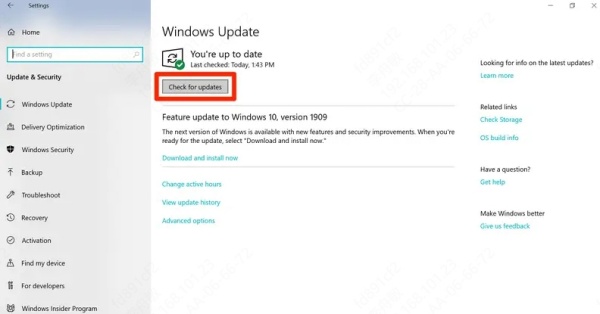
Fix 4.Check for Windows Updates
Some Windows updates include patches that improve hardware compatibility. If your GPU is not showing up due to a missing system patch, this step might solve it.
Why Updates Might Fix the Problem
Windows updates often include essential hardware patches. Go to:
Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update
Click Check for updates and install everything available.
Fix 5. Disable Integrated Graphics (If Applicable)
Many CPUs come with integrated graphics that may override your dedicated GPU. Disabling integrated graphics ensures Windows gives priority to your actual graphics card.
How to Disable from Device Manager or BIOS
Sometimes, your system prioritizes the integrated GPU. Disable it:
In Device Manager, under Display adapters, disable the Intel UHD or similar.
Or do it from BIOS by selecting the PCIe GPU as primary.
Fix 6. Check for Hardware Issues
If your GPU still isn't detected, it’s time to consider hardware-level problems. Testing the GPU in another system or using a different PCIe slot can help identify faulty hardware.
Test the GPU in Another System
If you have access to another PC, test the card there. If it’s still not recognized, the card itself might be faulty.
Try a Different PCIe Slot
Sometimes, a faulty slot is the culprit. Try inserting the card into another available PCIe slot and test again.
Fix 7. Registry Fixes (Advanced Users)
Windows registry stores hardware configuration settings. If something has gone wrong here, your GPU may be hidden or misconfigured. Advanced users can try tweaking the registry to fix this.
Back Up the Registry
Before editing, back up your registry:
Open regedit > File > Export.
Tweak Registry Keys Related to Display Adapters
Navigate to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\{4D36E968-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}
Delete UpperFilters and LowerFilters if they exist.
Fix 8. Power Supply Considerations
A weak or unstable power supply can prevent your GPU from initializing properly. Ensuring your PSU can handle your GPU’s power requirements is crucial for detection.
Is Your PSU Sufficient?
High-end GPUs require solid power delivery. Make sure your PSU is:
Adequate in wattage
Has the required 6/8-pin connectors
If the PSU is underpowered, the GPU might not initialize.
Conclusion
A missing GPU in Device Manager doesn’t always mean dead hardware. It could be a loose connection, BIOS misconfiguration, or corrupted driver. Go through the fixes step-by-step, and you’re likely to get it sorted without too much tech stress.
And if you need to solve graphics driver issues, don't hesitate to download Driver Talent for a free trial.
