A malfunctioning Intel Ethernet Driver cuts off your PC's wired connection to the internet or local network. Issues like Internet disconnections, "Unidentified Network" errors, or a complete lack of connectivity are almost always caused by an outdated, corrupted, or conflicting network driver, or interference from Windows power management settings.
Since a wired connection is often relied upon for stability and speed, resolving these driver issues quickly is essential. This guide provides systematic, step-by-step solutions for fixing your non-working Intel Ethernet driver, starting with the most efficient method for ensuring system stability.
Part I: Driver Integrity and System Synchronization
The Intel Ethernet controller relies on a clean, compatible driver and stable underlying motherboard Chipset drivers to function correctly. Conflicts here directly lead to connection failure.
Automated Driver Update with Driver Talent X
Manually troubleshooting and updating the specific Intel network driver, along with the core Chipset and power management drivers, can be complex and challenging when the internet connection is already lost. A specialized utility automates this entire procedure, guaranteeing stability for the network adapter.
Preparation:
Use a temporary internet connection (e.g., Wi-Fi adapter or mobile phone USB tether) if your PC is completely offline.
Download and install the Driver Talent X application onto your Windows PC.
Run Scan:
Launch the application and go to "Drivers" > "Scan", click "Scan".
The software will perform a deep analysis of your system, focusing on network and core system components.
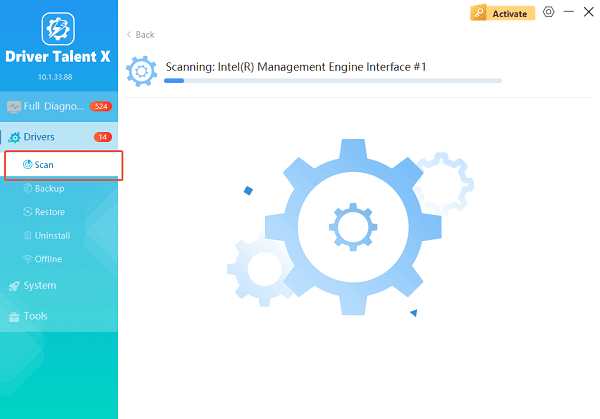
Execute Update:
After the scan is complete, the software will display a list of all drivers that need attention. Select the necessary drivers and click the "Upgrade" or "Repair Now" button.
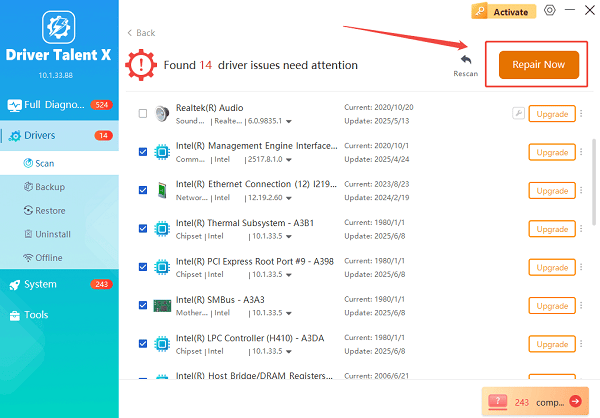
Driver Talent X will download the latest, certified versions specific to your Intel Ethernet controller, crucial for reliable connectivity.
Finalize:
After the installation is complete, restart your computer and check your wired internet connection.
Part II: Windows and Adapter Reinstallation Fixes
These solutions address software conflicts and power settings that prevent the adapter from working correctly.
Method 1: Reinstallation via Device Manager
This is the standard and most effective way to force Windows to remove the current problematic driver instance and load a fresh, clean version.
Press Windows Key + X and select "Device Manager".
Expand the "Network adapters" category.
Right-click on your Intel Ethernet Connection device.
Select "Uninstall device".
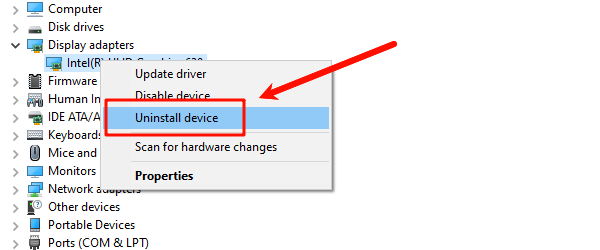
Crucially, check the box that says "Attempt to remove the driver software for this device".
In the Device Manager menu, click "Action" > "Scan for hardware changes". Windows will automatically detect the adapter and load a fresh driver copy.
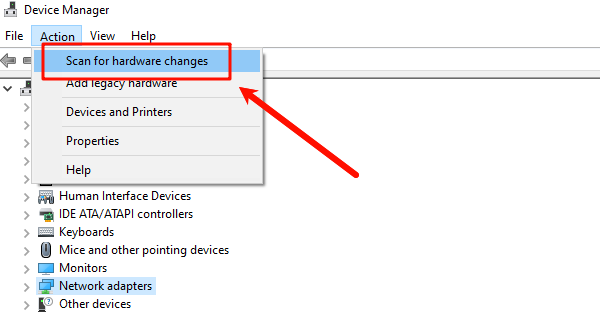
Method 2: Disable Power Management for the Ethernet Adapter
Windows power-saving features can aggressively shut down the Ethernet adapter to conserve power, causing intermittent disconnections or failures upon waking.
Press Windows Key + X and select "Device Manager".
Expand the "Network adapters" category.
Right-click on your Intel Ethernet adapter and select "Properties".
Go to the "Power Management" tab.
Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power".
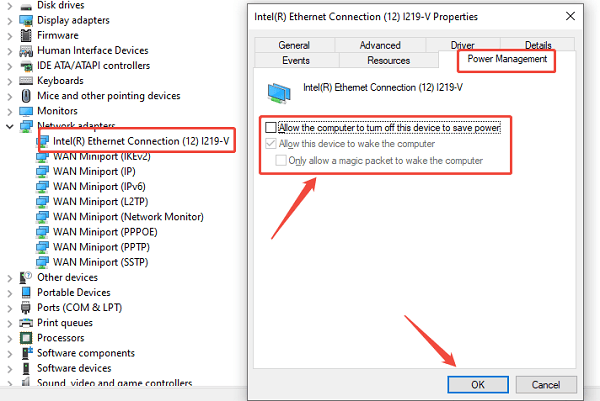
Click "OK".
Part III: Network Stack and System Configuration Fixes
These methods address deeper configuration issues within the Windows network stack.
Method 1: Reset the Windows Network Stack
Corrupted IP addresses, DNS settings, or Winsock files can prevent the adapter from obtaining a network address. A full reset often clears these issues.
Press Windows Key + I to open Settings.
Go to "Network & internet" > "Advanced network settings" > "Network reset".
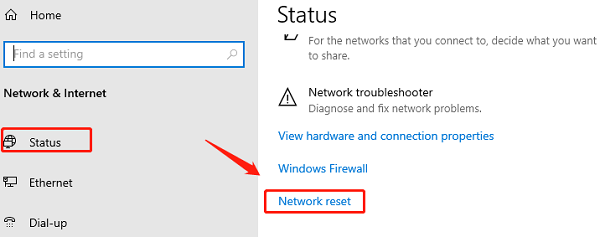
Click the "Reset now" button.
Restart your PC immediately after the reset is complete. (Note: You will lose saved Wi-Fi passwords and require a clean setup of any VPN or virtual adapter software.)
Method 2: Check and Update BIOS/UEFI
If the Ethernet adapter is a high-speed component (like 2.5G or 10G), it relies on the motherboard's firmware (BIOS/UEFI) to function correctly.
Check your motherboard manufacturer's website (ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, etc.) or the official Dell/HP/Lenovo support site for your model's latest BIOS update.
If an update is available, follow the manufacturer's instructions for flashing the new firmware. (This is an advanced step, requiring caution).
Conclusion
A non-working Intel Ethernet driver is a fixable problem rooted in driver corruption or power conflicts. The most reliable strategy is to first ensure system-wide driver synchronization and stability with Driver Talent X.
By combining this foundational fix with a clean reinstallation of the adapter via Device Manager and performing a full Windows Network reset, you can systematically eliminate the common causes and restore your stable, wired internet connection.
