When using Windows 10/11, some users may encounter a sudden program shutdown accompanied by a "KernelBase.dll crash" error message.
This type of error often affects the launch of games, the operation of productivity software, and can even cause overall system instability.
So, what is KernelBase.dll? Why does it crash? And how can you fix it? This article provides a comprehensive explanation along with detailed solutions.
1. What Is KernelBase.dll?
KernelBase.dll is one of the core components of the Windows operating system. It plays a key role in communication between applications and the system. Whenever a program tries to access system resources (such as memory, files, or APIs), it must pass through this DLL file. If KernelBase.dll becomes corrupted, missing, or is interfered with by third-party programs, crashes may occur.
2. Common Scenarios for KernelBase.dll Crashes
Crashes when launching games or large applications
Errors when using software such as Microsoft Office or Adobe
Error logs in Event Viewer point to KernelBase.dll
Certain programs fail to run properly after a Windows update
3. Causes of KernelBase.dll Crashes
Corrupted system files (including KernelBase.dll itself)
Incompatible third-party software or drivers
Incomplete or conflicting Windows updates
Registry errors or abnormal software configuration
Missing required runtime components (e.g., VC++ runtime)
4. Fixes for KernelBase.dll Crash Errors
Method 1: Use Professional Repair Software
Driver Talent X not only manages drivers but also includes DLL file repair functionality. It avoids manual file searches and installation mistakes.
Click the download button in the article to install the latest version of Driver Talent X and launch the program.
On first use, click "Try Now". The program will automatically scan your system's drivers and DLL file status.
Select "Full Checkup", find missing DLL files under the "Core DLL Files Abnormal" section, and click "Fix" to repair.
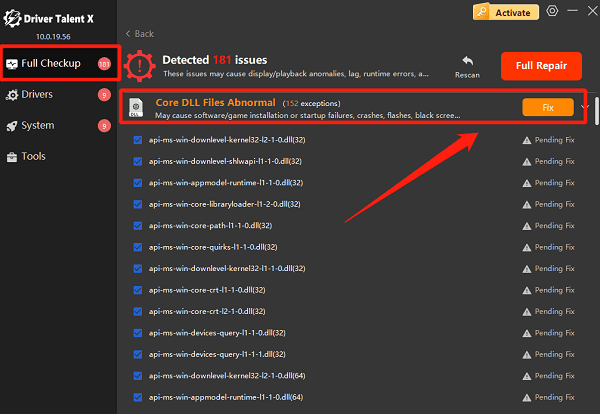
After the repair is complete, restart your PC to ensure the DLL files are properly loaded.
Method 2: Use System File Checker (SFC)
Press Win + S, search for "CMD", right-click Command Prompt, and select "Run as administrator".
In the command prompt, enter: sfc /scannow and press Enter.
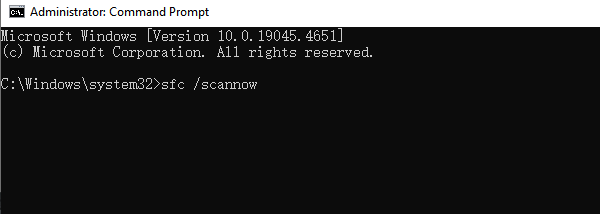
The command will scan and repair corrupted system files. This process may take a few minutes.
Once complete, if you see "Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them", restart your PC and check if the issue is resolved.
Method 3: Run the DISM Tool
If SFC doesn't fix the issue, try running the DISM command: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
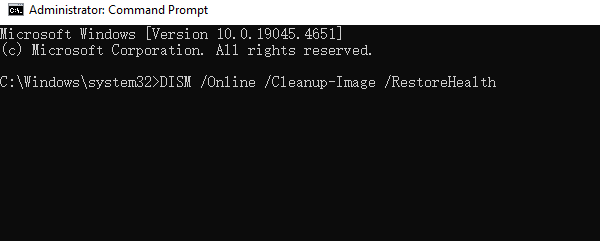
This command downloads and replaces corrupted system files from the Windows Update server, so an internet connection is required.
After running it, restart your computer and try running the problematic application again.
Method 4: Update Visual C++ Redistributables
Visit Microsoft's official download page via your browser.
Download the appropriate version for your system (32-bit or 64-bit):
For 32-bit: vc_redist.x86.exe
For 64-bit: vc_redist.x64.exe
Run the downloaded file and complete the installation.
Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Run the previously crashing program again to verify if the issue is fixed.
Method 5: Uninstall Problematic Software
Press Win + R, type "appwiz.cpl", and press Enter to open the Programs and Features window.
Find any recently installed or frequently crashing software in the list.
Right-click the program and select "Uninstall".
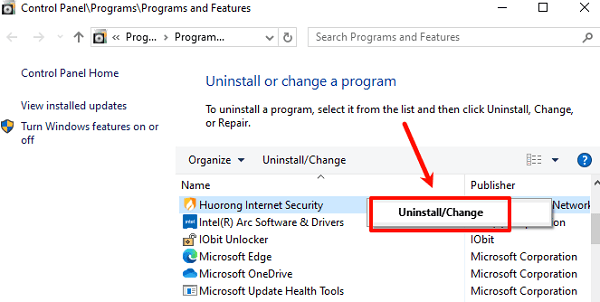
After uninstalling, restart your PC.
If necessary, visit the official website to download and reinstall the latest version.
If the issue persists, avoid reinstalling the software and contact the vendor's technical support.
Method 6: Create a New Windows User
Sometimes, a corrupted user profile can cause DLL errors:
Go to "Settings" > "Accounts" > "Family & other users".
Add a new user account.
Log in with the new account and check if the crash still occurs.
Although a KernelBase.dll crash may seem like a serious system failure, it is usually caused by third-party software or configuration issues.
By following the step-by-step troubleshooting methods above, most users can resolve the issue on their own. If none of these solutions work, consider restoring your system using a restore point or contact professional technical support.
