Some users may find that their WiFi network suddenly disappears on their laptop or desktop, no signal is detected, and even the home router becomes unconnectable.
This article analyzes common causes behind this issue and provides several effective solutions to help you quickly restore wireless connectivity.
I. Reasons Why WiFi Networks Don't Show Up
Wireless function is disabled: Some laptops have shortcut keys that can disable the wireless adapter.
Wireless driver is corrupted or outdated: Driver failures can prevent your device from detecting networks.
WLAN AutoConfig service is not running: Disabling this system service will directly impact wireless functions.
Router malfunction or weak signal: Long distances or improper router restarts may cause the network to disappear.
Incompatible network bands: Some devices only support 2.4GHz WiFi and cannot connect to 5GHz networks.
System updates or misconfiguration: Windows updates may alter network adapter settings.
II. Solutions to Fix WiFi Network Not Showing Up
Method 1: Update the Wireless Network Driver
Driver issues are a common cause of undetected WiFi networks. It's recommend to use the Driver Talent X tool, which automatically identifies, downloads, and installs the most compatible drivers for your device with minimal effort.
Click the Download button to get the latest version of Driver Talent X, then install and launch the software.
Go to the Drivers tab and click "Scan" to detect your PC's driver status.
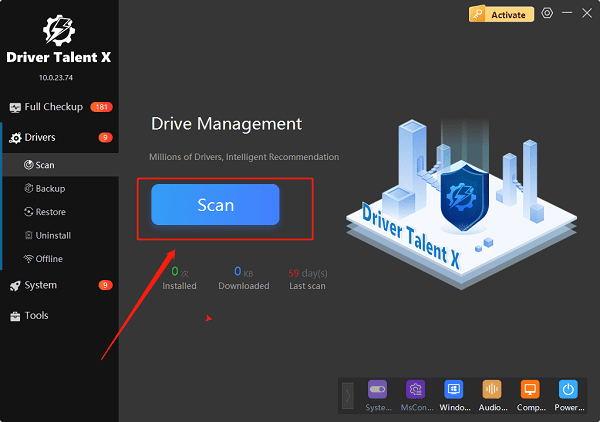
Locate your wireless driver in the results and click "Upgrade".
Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Method 2: Restart Devices and Check Wireless Function
Shut down your PC, then unplug the router's power supply. Wait 1–2 minutes before powering them back on.
Check whether your laptop has disabled WiFi using hotkeys like Fn + F2/F5/F12.
Ensure the WiFi icon in the lower-right taskbar isn't disabled. Re-enable it if necessary.
Method 3: Restart the WLAN AutoConfig Service
Press Win + R, type "services.msc", and hit Enter.
Find "WLAN AutoConfig" in the list.
Make sure its Status is "Running". Right-click and select "Restart".
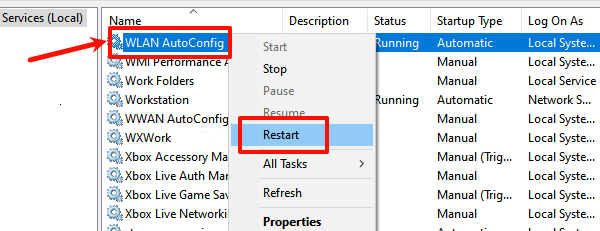
Double-click to open "Properties", then set the Startup type to "Automatic".
If not running, right-click and choose "Start".
Method 4: Connect to a Hidden WiFi Network
If your WiFi network has a hidden SSID:
Click the network icon in the taskbar > Manually Add Network.
Enter the full SSID, security type, and password.
Save and manually connect to the network.
Method 5: Run the Network Troubleshooter
Open Settings, then go to "Update & Security".
Choose Troubleshoot, then click "Additional Troubleshooters".
Find "Network Adapter" and click "Run the troubleshooter".
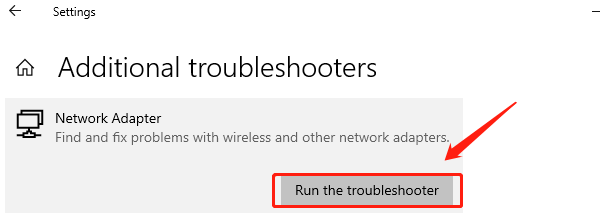
Follow the prompts to complete the repair process.
Method 6: Reset Network Settings
Open Settings (Win + I) and click "Network & Internet".
Select Status from the left panel, then scroll down and click "Network Reset".
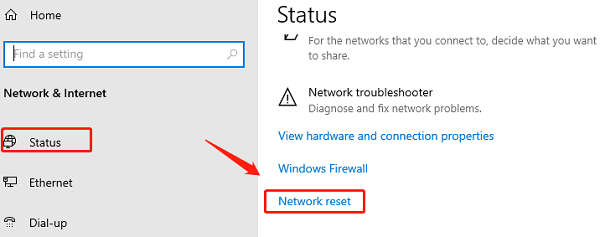
Click "Reset Now" and confirm.
The system will restart. Reconfigure your WiFi after reboot.
Method 7: Change Wireless Network Band
Some older devices can't detect 5GHz WiFi. Log into your router's admin panel and switch to 2.4GHz or Mixed Mode.
III. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: My phone connects to WiFi, but my PC can't. Why?
A: Your PC's WiFi might be off, the driver may be broken, or it doesn't support 5GHz. Turn WiFi back on or switch to 2.4GHz.
Q2: WiFi is gone after a Windows 11 update. What now?
A: The driver may not work with the new update. Try uninstalling the update or install a compatible driver.
Q3: No WiFi icon or settings?
A: Your WiFi adapter may be disabled. Go to Device Manager and turn it back on.
Although the issue of missing WiFi networks is common, most users can resolve it using the methods outlined in this guide. Driver updates and service checks are usually effective, while network reset is a good last resort.
If the issue persists, further hardware diagnostics or professional technical support may be necessary.
