For many users, upgrading or replacing a graphics card is a common way to improve computer performance. However, a frustrating issue some users encounter is that a newly installed AMD graphics card is not recognized, resulting in no display output or the system being unable to utilize the GPU's capabilities.
This article will explain the common causes and solutions for AMD graphics card detection issues, helping you restore system recognition and unlock the full performance of your graphics card.
1. Common Symptoms of an Unrecognized AMD Graphics Card
The system fails to boot or displays a black screen
Driver installation fails or has no effect
AMD graphics card does not appear in Device Manager
The card is recognized as "Microsoft Basic Display Adapter"
Games or applications cannot use the discrete GPU
2. Possible Causes
Improper installation or poor contact in the PCI-E slot
Missing or incompatible driver versions
Outdated BIOS or incorrect BIOS settings
Insufficient power supply causing GPU boot failure
Conflicts due to old drivers not being uninstalled
Windows failing to properly load the GPU device
3. Complete Solutions
Method 1: Check the Hardware Connection
Power off the PC and unplug the power cable.
Open the case and ensure the GPU is fully inserted into the PCI-E slot.

Make sure the power connectors (e.g., 6-pin/8-pin) are correctly plugged in.
Clean any dust from the slot and reseat the card.
Boot the PC and check for display output.
Tip: Re-seating the GPU usually resolves contact issues.
Method 2: Set the Discrete GPU as Priority
Enter BIOS setup (usually by pressing Delete or F2 during startup).
Find the "Initial Display Output" or similar option and set it to PEG/PCIe.
If integrated graphics are present, disable "Integrated Graphics (iGPU)".
Save changes and reboot.
If the BIOS is outdated, download the latest update from your motherboard's official site and follow the instructions to update it.
Method 3: Update the AMD Graphics Driver
Start by completely uninstalling old drivers in Safe Mode. For users unfamiliar with manual driver installations, it's recommended to use the Driver Talent X tool for efficient and easy driver management.
Click the download button to get the latest version of Driver Talent X, install and launch the software.
In the "Drivers" tab, select "Scan", and the software will automatically detect the status of all drivers.
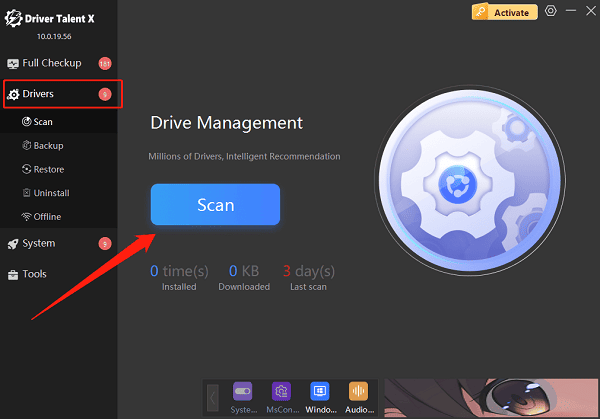
Locate the AMD graphics driver in the scan results and click "Upgrade".
After updating, restart the computer to ensure the driver takes effect.
Method 4: Manually Add Hardware via Device Manager
Press Win + X and select "Device Manager".
Expand "Display adapters" to see if there's an unknown device or only "Microsoft Basic Display Adapter".
Right-click the device and select "Update driver" > "Browse my computer for drivers".
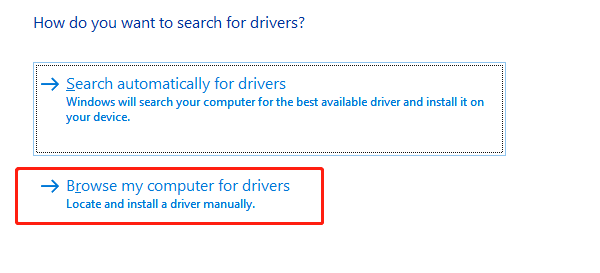
Navigate to the folder containing the AMD driver and install manually.
Restart the system once the device is recognized.
4. Additional Tips and Precautions
Ensure your power supply meets the GPU's requirements (at least 500W recommended).
Older motherboards may not support some newer GPU models.
Always back up important data before swapping hardware.
If the issue persists, test the GPU on another system to rule out hardware failure.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What should I do if my AMD GPU causes a black screen after installation?
A: Check if the GPU is properly seated and powered. Try resetting the BIOS or reinstalling the old GPU to update the BIOS.
Q2: How can I confirm if the system recognizes the GPU?
A: Check Device Manager to see if the GPU is listed correctly, or use third-party diagnostic tools.
Q3: Do I have to download drivers only from the official site?
A: It's recommended to get drivers from AMD's official site or use Driver Talent X for accurate and stable driver installation.
Although a newly installed AMD GPU not being recognized can be frustrating, most issues can be resolved by following the steps outlined in this article.
Don't forget to regularly update your drivers and BIOS to maintain system compatibility and optimal performance.
