While using Windows 11, many users may encounter a sudden blue screen error referencing the file "ntkrnlmp.exe". This type of BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) not only disrupts daily tasks but can also lead to frequent reboots and potential data loss.
This article will analyze the common causes of the ntkrnlmp.exe blue screen error in Windows 11 and provide several practical solutions to help you quickly restore system stability.
What Is ntkrnlmp.exe?
ntkrnlmp.exe stands for "Windows NT Kernel Multi Processor" and is a core part of the Windows operating system. It is responsible for system boot, hardware abstraction, memory management, and process scheduling.
When this file becomes corrupted or conflicts with drivers or hardware, it may result in system crashes and blue screen errors.
Common Causes of ntkrnlmp.exe Blue Screen Errors
| Type of Cause | Description |
| Driver conflicts | Outdated or incompatible drivers (like GPU, sound, or network) may conflict with ntkrnlmp.exe |
| Memory or disk issues | Faulty RAM, bad sectors on the hard drive, or file system errors |
| Failed Windows updates | Updates that weren't installed properly or contain compatibility issues |
| BIOS or overclocking | Improper overclocking or incorrect voltage/BIOS settings |
| Malware infection | Viruses or trojans that damage core system files or registry entries |
| Power management faults | CPU power state switching errors causing kernel crashes |
Solutions to Fix ntkrnlmp.exe Blue Screen in Windows 11
Method 1: Update Device Drivers
Driver issues are a leading cause of kernel crashes. It's recommend to use Driver Talent X, a tool that automatically detects and installs the correct drivers for your system.
Download the latest version of Driver Talent X and install it.
Open the software and go to the Drivers section, then click "Scan".
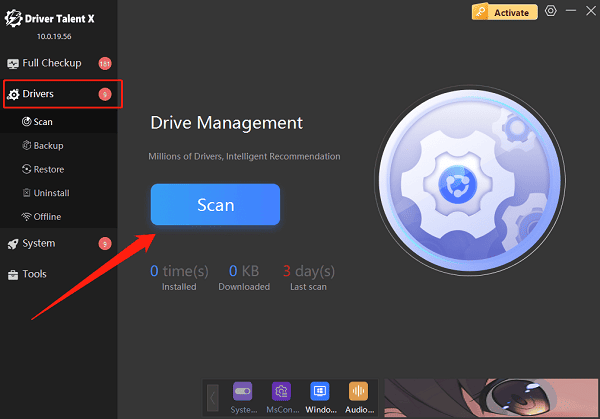
Find outdated or missing drivers in the results and click "Upgrade".
Restart your computer after the update to apply changes.
Method 2: Run Windows Memory Diagnostic
Press Win + R, type "mdsched.exe", and hit Enter.
Click "Restart now and check for problems (recommended)".
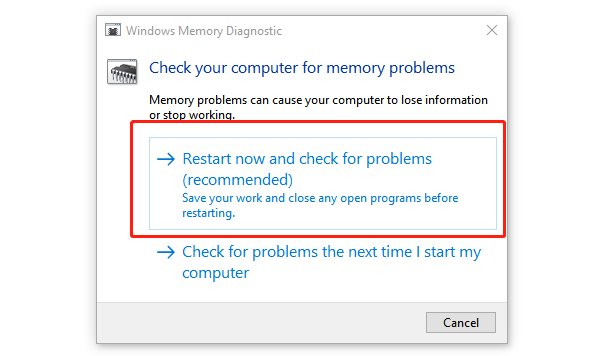
Your PC will reboot and scan for memory issues.
After the test, Windows will show the result via a notification.
Method 3: Check Hard Drive Health
Open Command Prompt as administrator.
Type: chkdsk C: /f /r and press Enter.
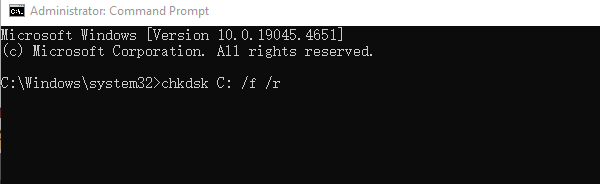
Type "Y" to schedule a check on the next reboot, then restart your PC.
Method 4: Adjust BIOS and Overclock Settings
Restart your computer and enter BIOS (usually by pressing F2 or DEL).
Select "Load Setup Defaults" to reset BIOS settings.
Disable CPU or RAM overclocking.
Save changes and restart.
If your BIOS version is outdated, visit your motherboard manufacturer's website to download the latest firmware.
Method 5: Use System File Checker (SFC)
Corrupt system files can trigger ntkrnlmp.exe errors.
Open Command Prompt as administrator.
Run: sfc /scannow
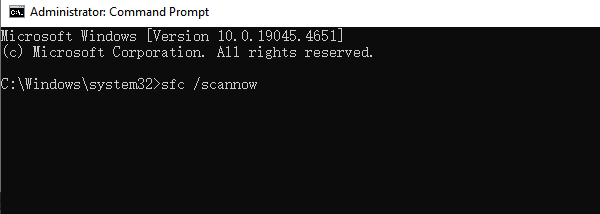
After it completes, restart your computer.
If issues persist, run: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
Method 6: Reset Windows
Press Win + I to open Settings.
Go to System > Recovery.
Under "Recovery" options, click Reset this PC > Reset PC.
Choose either "Keep my files" or "Remove everything".
Select "Cloud download" or "Local reinstall", then follow the on-screen instructions.
Note: Choosing "Remove everything" will erase all your files. Be sure to back up important data beforehand.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is the ntkrnlmp.exe blue screen caused by hardware?
A: Not always. It can be triggered by driver conflicts or hardware issues like faulty RAM or a failing hard drive.
Q2: Can I delete or replace the ntkrnlmp.exe file manually?
A: No. It's a critical system file. Modifying it manually could cause your system to crash completely.
Q3: The blue screen appears frequently, can I keep using my PC?
A: You should fix it immediately. Repeated BSODs may lead to hard drive corruption or other hardware damage.
The ntkrnlmp.exe blue screen error in Windows 11 is often related to drivers, memory, hard drive issues, or misconfigured system settings.
Fortunately, most of these problems can be resolved through driver updates, system scans, and hardware checks. It's recommended to keep your drivers and system up to date, back up your data regularly, and seek help from a professional technician if problems persist.
