A Lenovo laptop, failing to charge is a critical issue that can severely impact productivity. When your laptop shows "plugged in, not charging", or doesn't recognize the charger at all, the cause can range from simple faulty hardware connections to complex battery management software issues.
Addressing this problem requires a systematic approach, often beginning with software and driver checks that govern power management. This guide provides step-by-step solutions to diagnose and fix why your Lenovo laptop is not charging.
Part I: Driver and System Conflicts
The most common causes for charging failure (especially if the charger and outlet are functional) are corrupted power management drivers or outdated BIOS firmware that fails to communicate the charge status correctly.
Method 1: Automated Driver Update with Driver Talent X
Manually updating the battery, power management (ACPI), and chipset drivers can be complex. A specialized utility is the fastest way to ensure all necessary system drivers and power components are current and compatible, resolving deep-seated conflicts.
Download and Install:
Click the "Download" button to download the software package.
Install it on your Lenovo laptop.
Run Scan:
Launch the application and go to "Drivers" > "Scan", click "Scan".
The software will perform a comprehensive analysis of all hardware, including the battery, chipset, and power management controllers.
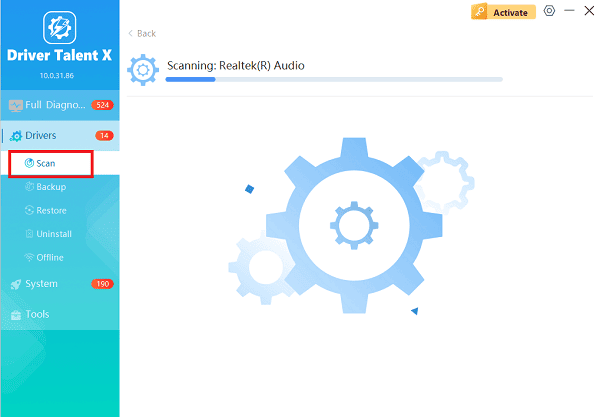
Install the Update:
After the scan is complete, the software will display a list of all drivers that need attention. Select the necessary power and system drivers and click the "Repair Now" button.
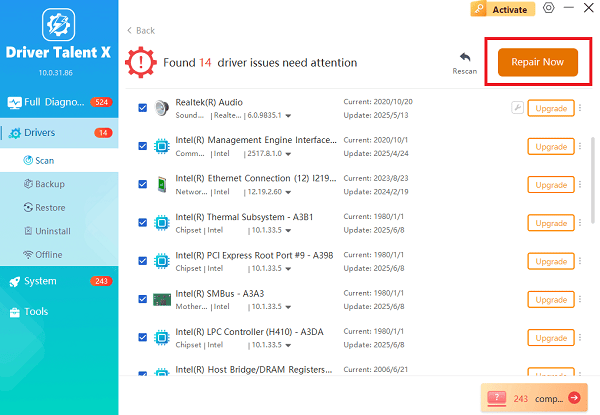
Driver Talent X will download the latest, certified versions specific to your Lenovo model and Windows OS.
Finalize:
After the installation is complete, restart your computer and check the charging status.
Method 2: Uninstall the ACPI Battery Driver
Windows can sometimes miscommunicate with the battery through the ACPI driver. A forced reinstallation often fixes this communication.
Press Windows Key + X and select "Device Manager".
Expand the "Batteries" category.
Right-click on "Microsoft ACPI Compliant Control Method Battery".
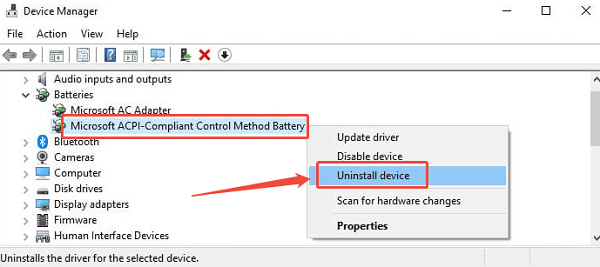
Select "Uninstall device". Do NOT check the box to delete the driver software.
In the Device Manager menu, click "Action" > "Scan for hardware changes". Windows will automatically reinstall the driver.
Restart the laptop and test charging.
Part II: Hardware and Physical Checks
These steps address physical faults in the charger, cable, and power port.
Method 1: Perform a Power Drain (Hard Reset)
A hard reset clears residual electrical charge (flea power) that can confuse the motherboard's power controllers.
Unplug Everything: Power down the laptop completely. Unplug the AC adapter and remove the battery if your model has a removable battery.
Hold Power Button: Press and hold the laptop's main power button for 30 to 40 seconds. This drains all residual charge.
Test: Reconnect the AC adapter (without the battery, if removable) and attempt to power on the system and check the charging light.
Method 2: Inspect Charger and Port
If the system isn't recognizing the charger at all, the fault is likely physical.
Inspect Adapter: Check the entire length of the charger cable and the power brick for fraying, bending, or damage.

Check Port: Shine a light into the charging port (DC jack or USB-C port) on the laptop. Look for bent pins, debris, or looseness. If the port is loose, it often indicates a connection issue that requires repair.
Test Outlet: Plug the charger into a different, confirmed working wall outlet to rule out a faulty power source.
Part III: Lenovo and BIOS Settings
Lenovo includes proprietary software settings that can intentionally prevent the battery from charging fully or at all.
Method 1: Disable Battery Conservation Mode
Lenovo Vantage software often includes a "Conservation Mode" designed to extend battery lifespan by limiting the charge level to 50-60%.
Open the Lenovo Vantage application (pre-installed on most Lenovo laptops).
Navigate to "My Device Settings" > "Power".
Find the setting for "Conservation Mode", "Battery Gauge Reset" or "Battery Health Mode".
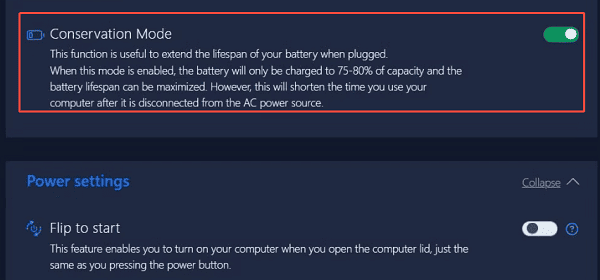
If Conservation Mode is enabled, disable it. This allows the battery to charge up to 100%.
Method 2: Update BIOS/UEFI Firmware
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) manages all hardware functions, including charging. An outdated BIOS may contain bugs related to power management.
Go to the official Lenovo Support website.
Enter your laptop's serial number or model name.
Search for available BIOS/UEFI Firmware updates.
Download the latest update and follow Lenovo's instructions precisely (usually by running an executable file and ensuring the laptop is plugged in during the process). Warning: Do not interrupt a BIOS update.
Conclusion
A Lenovo laptop failing to charge is usually a solvable problem, with the fix often lying in the software layer. The most reliable solution is ensuring power management and chipset drivers are stable with Driver Talent X. By combining this with a Power Drain and checking the Lenovo Vantage Conservation Mode, you can systematically eliminate the most common charging obstacles.
