Intel processors are widely used in desktops and laptops due to their strong performance, stability, and broad software compatibility. However, many users do not fully utilize their Intel CPU's capabilities because of outdated drivers, incorrect system settings, or poor thermal and power management. This guide explains what an Intel processor is and provides detailed, practical steps to maximize its performance on Windows systems.
Step 1: Update Intel Drivers First Using Driver Talent X
Keeping Intel chipset, graphics, and management engine drivers up to date is critical. Outdated or incompatible drivers can limit CPU performance, cause instability, or prevent advanced features from working correctly.
Download and Install:
Click the "Download" button to download the installer to your computer.
Run the installer, follow the on-screen instructions, choose the installation path, and complete the setup.
Scan for Driver Issues:
Open Driver Talent X from the desktop shortcut or Start menu and go to "Drivers" > "Scan", click "Scan".
Driver Talent X will detect outdated, missing, corrupted, or incompatible drivers, including Intel graphics, chipset, WiFi, Bluetooth, and audio drivers.
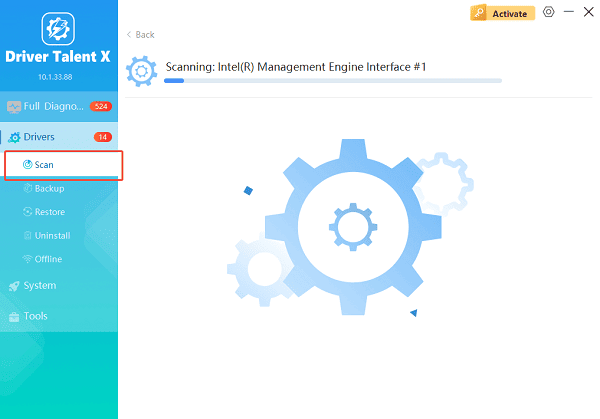
Update All Drivers:
Wait for the scan to complete. The tool will automatically detect outdated, missing, corrupted, or incompatible drivers.
Select the necessary drivers and click the "Upgrade" or "Repair Now" button. Driver Talent X will download the correct driver version for your motherboard and operating system.

Restart Your Computer:
Allow the installation process to finish without interruption.
Restart your computer to ensure the updated drivers are fully applied.
Updating these drivers ensures proper CPU power management, correct communication between hardware components, and better overall system responsiveness.
What Is an Intel Processor?
An Intel processor, also known as a CPU, is the main component responsible for executing instructions, running applications, and managing system tasks. Modern Intel CPUs include multiple cores, threads, turbo boost technology, and integrated graphics on many models. Performance depends not only on the CPU itself but also on drivers, BIOS settings, cooling, and Windows configuration.
Step 2: Enable High Performance Power Plan
Windows power settings can limit CPU frequency to save energy.
How to Change Power Plan:
Press Windows + R, type "control", and press Enter.
Go to Hardware and Sound > Power Options.
Select "High performance" or "Ultimate Performance" if available.
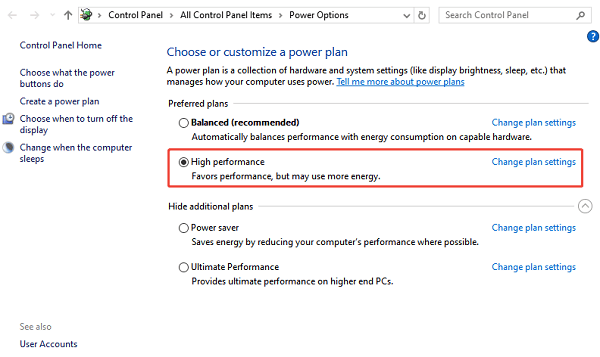
Restart your system.
This allows the Intel processor to run at higher clock speeds when needed.
Step 3: Optimize Intel Turbo Boost and BIOS Settings
Intel Turbo Boost dynamically increases CPU speed under load, but it can be disabled or limited.
What to Check in BIOS:
Restart your PC and enter BIOS by pressing F2, Delete, or F10 during startup.
Locate CPU or Advanced settings.
Ensure "Intel Turbo Boost" is enabled.
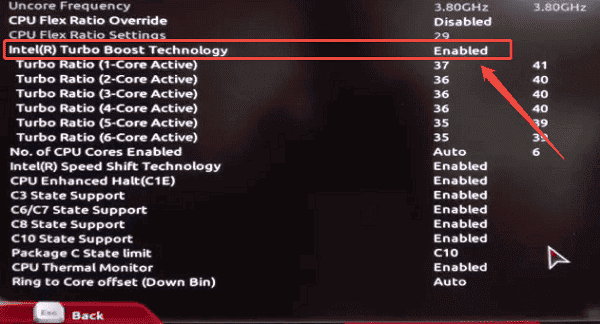
Check CPU power limits (PL1 and PL2) if available and keep them at default or manufacturer-recommended values.
Save changes and exit BIOS.
Incorrect BIOS settings can significantly reduce CPU performance.
Step 4: Improve Cooling and Thermal Management
Intel processors automatically reduce speed when temperatures are too high.
Practical Cooling Tips:
Clean dust from fans and vents.
Ensure laptop air intakes are not blocked.
Replace thermal paste on older desktops if temperatures are consistently high.
Use a laptop cooling pad for sustained workloads.
Lower temperatures allow the CPU to maintain higher boost clocks for longer periods.
Step 5: Reduce Background Processes and Startup Programs
Excess background apps consume CPU resources.
How to Optimize Startup:
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
Go to the Startup tab.
Disable unnecessary programs.
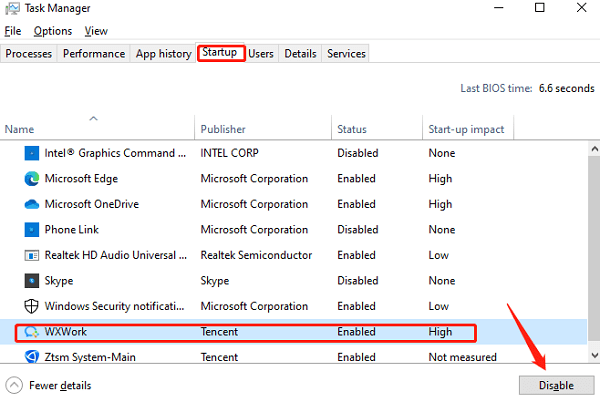
Restart the computer.
This frees CPU resources for tasks that matter.
Step 6: Keep Windows Updated
Windows updates often include performance optimizations for Intel processors.
Open Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
Click "Check for updates", install all recommended updates.
Restart if prompted.
Step 7: Use Intel Software Utilities When Applicable
Some Intel systems support tools such as Intel Graphics Command Center or Intel Extreme Tuning Utility.
Use them only if officially supported by your CPU and motherboard.
Avoid aggressive overclocking on laptops, as it may cause overheating or instability.
Conclusion
An Intel processor delivers strong performance when properly configured, but driver updates, power settings, cooling, and system optimization all play essential roles. Updating Intel drivers first using Driver Talent X provides a stable foundation, ensuring your CPU communicates correctly with Windows and other hardware components.
By combining driver updates with BIOS optimization, thermal management, and Windows tuning, you can safely maximize the performance of your Intel processor for daily work, gaming, or professional tasks.
